The Role of an ENT Specialist in Modern Medicine
Otolaryngologists, commonly known as ENT specialists, play a critical role in diagnosing and treating conditions related to the ear, nose, throat, and structures of the head and neck. Their expertise spans multiple disciplines, making them vital in both medical and surgical treatments. Patients of all ages, from infants to the elderly, seek their care for various conditions that impact essential functions such as breathing, hearing, swallowing, and speech.
The scope of otolaryngology is vast, covering disorders that range from minor infections to life-threatening cancers. This specialty incorporates both medical and surgical approaches, providing a comprehensive treatment strategy for a wide range of conditions. Unlike many other specialties that rely heavily on referrals, ENT specialists often manage the entire treatment process, from diagnosis to post-operative care.
A significant portion of their work involves conditions that affect sensory functions, including balance, hearing, and smell. Given the complexity of the human head and neck, ENT specialists frequently collaborate with neurologists, oncologists, allergists, and speech therapists to ensure well-rounded patient care.
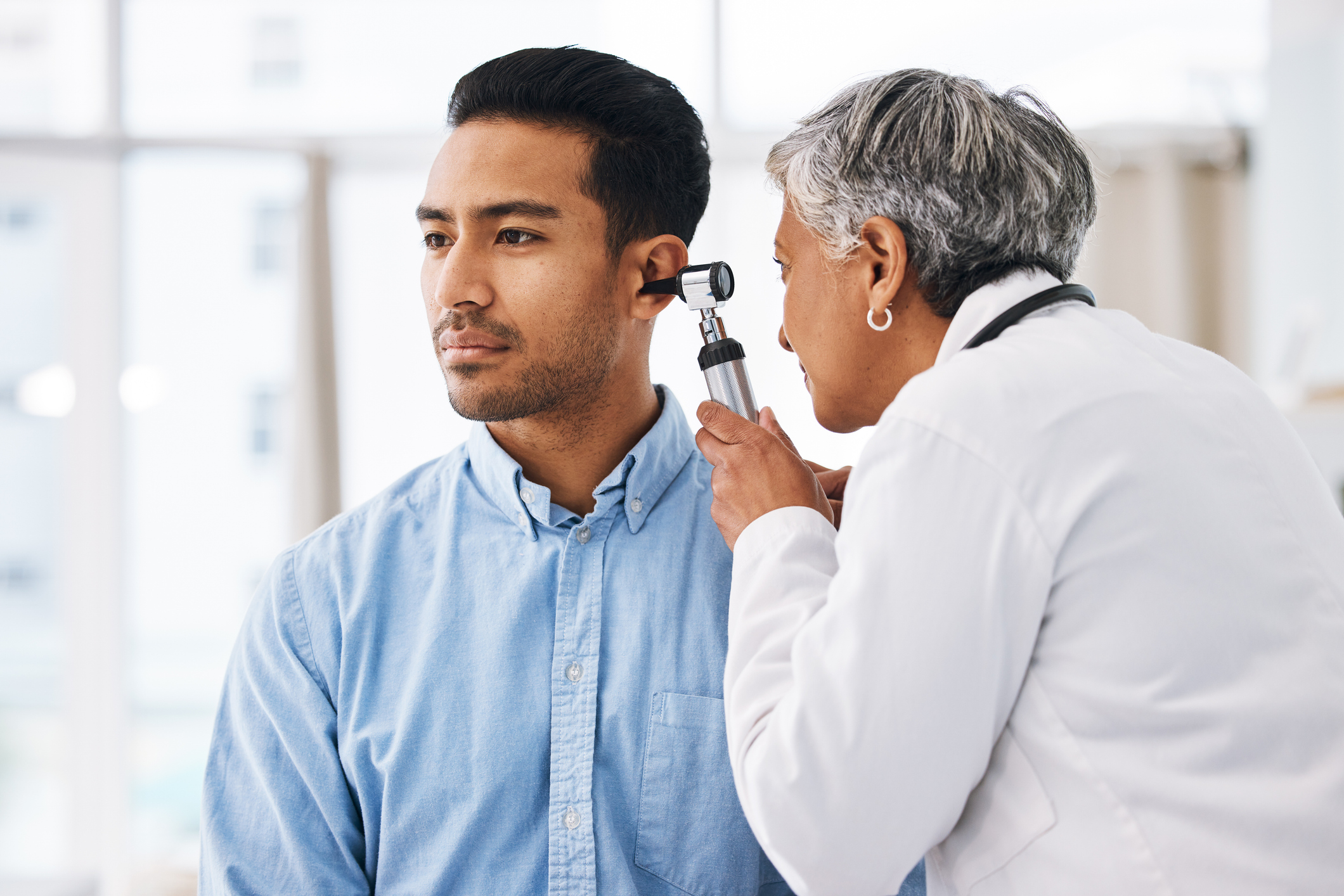

Medical and Surgical Expertise of Otolaryngologists
Treatment of Ear-Related Disorders
ENT specialists diagnose and treat a variety of ear-related conditions that impact hearing, balance, and neurological function. Common issues include chronic ear infections, hearing loss, tinnitus, and vertigo. Ear disorders are particularly prevalent in young children, and untreated infections can lead to long-term hearing impairment or speech development delays.
Chronic ear infections are a frequent concern, often requiring medical management or surgical intervention. One of the most common procedures is tympanoplasty, which repairs eardrum perforations. For patients experiencing hearing loss, an otolaryngologist may recommend hearing aids or cochlear implants, depending on the severity of the condition.
Balance disorders also fall under the expertise of ENT specialists. Vertigo and dizziness often stem from issues in the inner ear, and conditions such as Ménière’s disease require targeted treatments to improve stability and reduce symptoms.
Nasal and Sinus Health
The nasal passages and sinuses play a crucial role in respiratory health. ENT specialists are highly skilled in diagnosing and treating conditions that impact breathing, smell, and sinus function. Chronic sinusitis, nasal polyps, and a deviated septum are among the most commonly treated conditions.
Chronic sinusitis affects millions of people each year, causing persistent congestion, headaches, and facial pain. When medical treatments such as antibiotics or nasal steroids prove ineffective, procedures like endoscopic sinus surgery may be necessary. This minimally invasive technique removes blockages and improves airflow, providing long-term relief for patients.
Nasal fractures and injuries also fall under the domain of ENT specialists. A broken nose or structural abnormalities can lead to breathing difficulties and aesthetic concerns. Surgical procedures such as septoplasty or rhinoplasty may be performed to restore proper function and appearance.
Throat and Laryngeal Disorders
The throat serves multiple essential functions, including swallowing, speech, and airway protection. ENT specialists manage a range of throat conditions, from mild infections to complex disorders affecting vocal cords and esophageal function.
Patients experiencing voice changes, hoarseness, or difficulty swallowing may have underlying conditions such as laryngitis, vocal cord nodules, or gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). These conditions can be managed through lifestyle modifications, medication, or surgical interventions.
Chronic tonsillitis and adenoid infections are common reasons for ENT consultations, particularly in children. In cases where infections are recurrent, a tonsillectomy or adenoidectomy may be recommended. These procedures help prevent future infections and improve overall respiratory health.
Head and Neck Surgery
ENT specialists treat both benign and malignant conditions affecting the head and neck. This includes thyroid and parathyroid disorders, salivary gland diseases, and various forms of cancer. Given the complexity of these structures, precision is essential when performing surgical procedures.
Head and neck cancers require comprehensive treatment plans that often include surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. ENT specialists play a key role in tumor removal and reconstructive procedures that restore function and aesthetics. Neck dissection, a procedure performed to remove cancerous lymph nodes, is a common surgical intervention in these cases.
Thyroid and parathyroid disorders are also managed by otolaryngologists. Conditions such as hyperthyroidism or thyroid nodules may require partial or total thyroidectomy, depending on the severity of the disease. Advanced techniques allow for minimally invasive approaches, reducing recovery time and post-operative complications.
Facial Reconstructive and Plastic Surgery
Facial plastic surgery is another specialized area within otolaryngology. ENT specialists perform reconstructive procedures for congenital anomalies, trauma-related injuries, and cosmetic enhancements.
Reconstructive surgery is essential for patients who have experienced facial trauma or undergone tumor removal. Procedures such as cleft palate repair, scar revision, and facial nerve reconstruction help restore both function and appearance.
Cosmetic procedures, including rhinoplasty and facelift surgeries, are also performed by ENT specialists. These procedures address structural concerns while enhancing facial aesthetics. In some cases, cosmetic interventions can improve breathing function, particularly when correcting a deviated septum or nasal obstructions.
Common Conditions Treated by ENT Specialists
Chronic Sinusitis and Allergies
Sinus infections and allergies are among the most frequent reasons patients seek ENT care. Persistent inflammation in the sinuses can lead to chronic sinusitis, causing symptoms such as facial pain, nasal congestion, and difficulty breathing. Allergies exacerbate these issues, triggering inflammation and excessive mucus production.
Treatment options range from medication to surgical interventions. Sinus surgery is often performed when traditional treatments fail to provide relief. Allergy testing and immunotherapy are also available for patients with severe allergic reactions affecting the nasal passages.
Hearing Loss and Tinnitus
Hearing loss affects individuals of all ages, with causes ranging from genetic conditions to prolonged noise exposure. Otolaryngologists assess hearing function through diagnostic tests and recommend appropriate treatment options, including hearing aids or surgical implants.
Tinnitus, the perception of ringing or buzzing sounds in the ears, is another common issue managed by ENT specialists. While there is no definitive cure, various treatment approaches, including sound therapy and medication, can help alleviate symptoms.
Swallowing and Speech Disorders
Dysphagia, or difficulty swallowing, can arise from various conditions affecting the throat and esophagus. ENT specialists evaluate swallowing function through imaging studies and endoscopic examinations. Treatment may involve dietary modifications, speech therapy, or surgical procedures to correct underlying anatomical issues.
Speech disorders related to vocal cord dysfunction or neurological conditions also require specialized treatment. Voice therapy, surgical interventions, and medication are commonly used to improve vocal function and communication ability.
Sleep-Related Breathing Disorders
Sleep apnea and snoring are significant health concerns that affect quality of life and increase the risk of cardiovascular disease. ENT specialists evaluate airway obstruction and offer treatment options, including CPAP therapy, surgical interventions, and lifestyle modifications.
Surgical treatments for sleep apnea include uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP) and radiofrequency ablation, which help open the airway and reduce obstruction. These procedures can improve breathing patterns and enhance sleep quality.
ENT Training and Certification
Becoming an ENT specialist requires extensive education and training. After completing medical school, aspiring otolaryngologists must undergo five to seven years of residency training. During this period, they gain hands-on experience in medical and surgical treatments for ear, nose, and throat disorders.
Board certification is an essential step in becoming a recognized specialist. Candidates must pass rigorous examinations to demonstrate proficiency in otolaryngology. Subspecialty training is available for those interested in areas such as pediatric otolaryngology, head and neck oncology, or facial plastic surgery.
Continuing education is crucial for ENT specialists, as advancements in technology and treatment approaches continue to evolve. Many professionals engage in research and clinical trials to contribute to the field’s ongoing development.
Education, Training, and Certification for ENT Specialists
Becoming an otolaryngologist requires an extensive commitment to education and training. The path to becoming an ENT specialist spans approximately 15 years, beginning with an undergraduate degree, followed by medical school, and concluding with rigorous residency and fellowship programs for those pursuing subspecialties. ENT physicians must develop expertise in both medical and surgical treatments, requiring hands-on experience across a broad range of conditions affecting the head and neck.
Undergraduate Education and Medical School
The journey starts with an undergraduate degree, typically lasting four years. While medical schools do not require a specific major, most aspiring doctors choose to study biology, chemistry, or another pre-medical field to fulfill medical school prerequisites. Coursework in anatomy, physiology, microbiology, and biochemistry provides a strong foundation for future medical training. Many students also engage in clinical experience, shadowing physicians or participating in research projects related to head and neck conditions, which can be beneficial when applying to medical school.
After completing a bachelor’s degree, students must take the Medical College Admission Test (MCAT) and gain acceptance into medical school. Medical school typically lasts four years, divided into two years of foundational coursework in the basic sciences and two years of clinical rotations. During clinical years, medical students gain exposure to different specialties, including otolaryngology, and many take the opportunity to complete an ENT rotation to confirm their interest in the field.
Otolaryngology Residency Training
After earning a Doctor of Medicine (M.D.) or Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine (D.O.), graduates enter residency training, which lasts at least five years. Otolaryngology residency programs are highly competitive, and applicants must have strong medical school performance, high scores on the United States Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) or COMLEX-USA, and relevant research experience.
The first year of residency, often called the internship year, includes general surgical training in areas such as general surgery, critical care, anesthesiology, and emergency medicine. This foundation prepares residents for the more specialized training that follows.
The remaining four years of residency focus exclusively on otolaryngology-specific education and surgical training. Residents gain hands-on experience diagnosing and treating conditions affecting the ear, nose, throat, head, and neck. They learn to manage sinus disorders, hearing loss, throat cancers, voice disorders, and structural abnormalities. During this period, residents also participate in operating room procedures, research projects, and clinical practice under the supervision of experienced ENT surgeons.
Board Certification and Licensure
Upon completing residency, otolaryngologists must obtain board certification and licensure before practicing independently. Physicians must pass the American Board of Otolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery (ABOHNS) board exam, which consists of both written and oral examinations. The written portion tests knowledge of medical and surgical management of ENT disorders, while the oral exam evaluates clinical decision-making and problem-solving skills.
For osteopathic physicians (DOs), certification is available through the American Osteopathic Board of Ophthalmology and Otolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery (AOBOO-HNS). Osteopathic otolaryngologists must complete an accredited osteopathic residency program in otolaryngology and pass board examinations to achieve certification. More details about the certification process can be found on the AOBOO-HNS website.
Exploring Medical Specialties and Career Paths for Doctors
Choosing a medical specialty is one of the most significant decisions a physician makes. Some doctors are drawn to surgical fields such as otolaryngology, while others prefer non-surgical disciplines like internal medicine or psychiatry. The decision often depends on factors such as earning potential, residency competitiveness, and overall job satisfaction. Each specialty comes with unique challenges and rewards, making it essential for aspiring physicians to consider what aligns best with their skills, interests, and long-term goals.
The Highest Paid Specialties in Medicine
Physicians who enter certain fields often see higher salaries due to the complexity of procedures, patient demand, and level of expertise required. Specialties such as neurosurgery, orthopedic surgery, plastic surgery, and cardiology consistently rank at the top in terms of compensation. These high-paying specialties often require years of additional training beyond medical school and residency, as well as a significant investment in technical skill and precision.
For those considering an ENT career, subspecialties such as neurotology and facial plastic surgery are among the more lucrative options. Otolaryngologists specializing in head and neck surgery or complex reconstructive procedures may also achieve higher earning potential.
To explore the highest paid specialties in the United States and see how salaries compare across medical fields.
Competitive Specialties and Match Rates
Not all medical specialties are equally accessible. Some are highly competitive, requiring exceptional academic performance, research experience, and top-tier USMLE or COMLEX scores to secure a residency position. Fields such as dermatology, plastic surgery, orthopedic surgery, and neurosurgery have some of the lowest match rates, making them particularly difficult to enter.
Otolaryngology falls into the moderately competitive category, with a limited number of residency slots each year. Applicants must demonstrate strong clinical skills, research experience, and excellent board scores to match successfully. In contrast, specialties such as family medicine, internal medicine, and psychiatry have higher match rates, providing more opportunities for graduates who may not wish to enter highly specialized or procedural fields.
For an in-depth look at match rates for competitive medical specialties and insights into the least competitive fields.
Specialties Known for High Job Satisfaction
While salary and competitiveness play a role in choosing a specialty, many physicians prioritize work-life balance, career fulfillment, and job satisfaction. Some fields naturally lend themselves to lower stress levels and predictable schedules, while others are more demanding.
Specialties such as dermatology, ophthalmology, and emergency medicine consistently rank among the five happiest medical specialties due to flexible schedules, engaging patient interactions, and lower burnout rates. Physicians in these fields often enjoy a balanced professional and personal life, making them attractive choices for those who value lifestyle considerations alongside their medical career.
To learn more read about the five happiest medical specialties and what makes them ideal for long-term job satisfaction.
Finding the Right Specialty Fit
Every medical specialty offers unique opportunities and challenges. Some physicians prioritize higher salaries and financial security, while others seek job satisfaction and a sustainable work-life balance. For those pursuing highly competitive fields, early preparation and strong academic performance are crucial. Aspiring ENT specialists must consider subspecialization options that align with their skills and interests, whether in facial plastic surgery, neurotology, or pediatric otolaryngology.
By carefully evaluating factors such as salary potential, competitiveness, and job satisfaction, medical students and residents can make informed decisions about their future in medicine.
Subspecialty Training and Fellowships
While residency provides comprehensive ENT training, some physicians choose to pursue further specialization by completing a one- to two-year fellowship. These programs allow otolaryngologists to develop expertise in highly specialized areas of ENT medicine, including:
- Pediatric Otolaryngology – Focuses on ENT disorders in children, including congenital airway abnormalities, recurrent ear infections, and hearing loss.
- Reconstructive and Facial Plastic Surgery – Specializes in cosmetic and functional facial surgeries, including rhinoplasty, cleft palate repair, and trauma reconstruction.
- Laryngology – Concentrates on disorders of the voice, swallowing, and airway, including vocal cord paralysis, GERD-related throat conditions, and laryngeal cancer.
- Sleep Medicine – Deals with conditions such as obstructive sleep apnea and snoring, requiring expertise in airway anatomy and surgical interventions.
- Allergy – Focuses on the management of seasonal and chronic allergies, including immunotherapy and other medical treatments.
- Rhinology – Specializes in sinus and nasal disorders, including complex sinus surgeries, polyp removal, and skull base tumors.
- Otology and Neurotology – Addresses hearing and balance disorders, including cochlear implants, skull base surgery, and inner ear conditions.
- Head and Neck Surgery – Involves complex surgical management of tumors, thyroid and parathyroid diseases, and reconstructive surgery for cancer patients.
ENT specialists who complete a fellowship gain additional expertise, increase career opportunities, and may earn higher salaries in specialized practice settings.
Continuing Medical Education and Advancements in ENT Medicine
Even after certification, ENT specialists must engage in continuing medical education (CME) to stay updated on advancements in the field. Emerging minimally invasive surgical techniques, robotic-assisted procedures, and advancements in hearing restoration technology continuously shape otolaryngology. Participation in conferences, research, and clinical trials allows ENT specialists to integrate the latest medical innovations into their practice.
Many ENT physicians also become involved in teaching, academic research, or hospital leadership roles. Some go on to develop new surgical techniques, author textbooks, or lead medical organizations. By staying current in their field, ENT specialists ensure that they provide the highest quality care for their patients.
The Path to Becoming an ENT Specialist
The journey to becoming an otolaryngologist is long and demanding, but it offers a highly rewarding career. ENT specialists combine medical expertise with surgical skill, providing a unique opportunity to diagnose, treat, and even surgically correct conditions affecting vital sensory and respiratory functions.
With cutting-edge advancements in medical technology, new treatment approaches, and a growing demand for ENT care, otolaryngology remains one of the most dynamic and fulfilling medical specialties. Physicians who pursue this path gain diverse career opportunities, from general ENT practice to highly specialized surgical fields. The extensive training and certification process ensures that ENT specialists are well-equipped to handle the complex and evolving challenges of head and neck medicine.
The Impact of ENT Specialists in Healthcare
ENT specialists provide essential medical and surgical care for a wide range of conditions affecting the head and neck. Their expertise in treating hearing loss, sinus diseases, throat disorders, and facial trauma makes them invaluable in modern medicine. Whether managing chronic conditions or performing complex surgeries, otolaryngologists are crucial in improving patient health and quality of life.
With ongoing advancements in diagnostic techniques and treatment options, ENT specialists continue to refine their skills and expand their capabilities. Patients seeking relief from ear, nose, and throat conditions can benefit from the specialized care these highly trained medical professionals provide.
If you are a student interested in becoming an ENT specialist, we encourage you to apply to our Pre-Medical Internship Program.